Add a database context
The database context is the main class that coordinates Entity Framework functionality for a data model. This class is created by deriving from the Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.DbContext class.
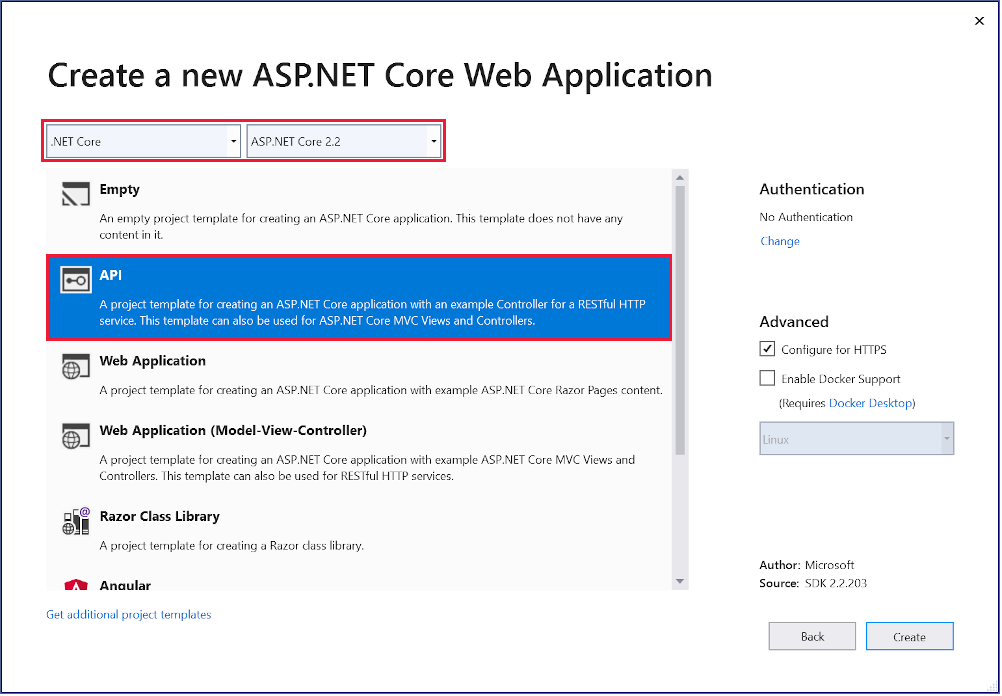
- Right-click the Models folder and select Add > Class. Name the class TodoContext and click Add.
Replace the template code with the following code:
namespace TodoApi.Models
{
public class TodoContext : DbContext
{
public TodoContext(DbContextOptions<TodoContext> options)
: base(options)
{
}
public DbSet<TodoItem> TodoItems { get; set; }
}
}
Register the database context
In ASP.NET Core, services such as the DB context must be registered with the
dependency injection (DI) container. The container provides the service to controllers.
Update Startup.cs with the following highlighted code:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using TodoApi.Models;
namespace TodoApi
{
public class Startup
{
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration)
{
Configuration = configuration;
}
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; }
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddDbContext<TodoContext>(opt =>
opt.UseInMemoryDatabase("TodoList"));
services.AddMvc().SetCompatibilityVersion(CompatibilityVersion.Version_2_2);
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
else
{
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseMvc();
}
}
}
The preceding code:
- Removes unused
using declarations.
- Adds the database context to the DI container.
- Specifies that the database context will use an in-memory database.
Add a controller
Right-click the Controllers folder.
Select Add > New Item.
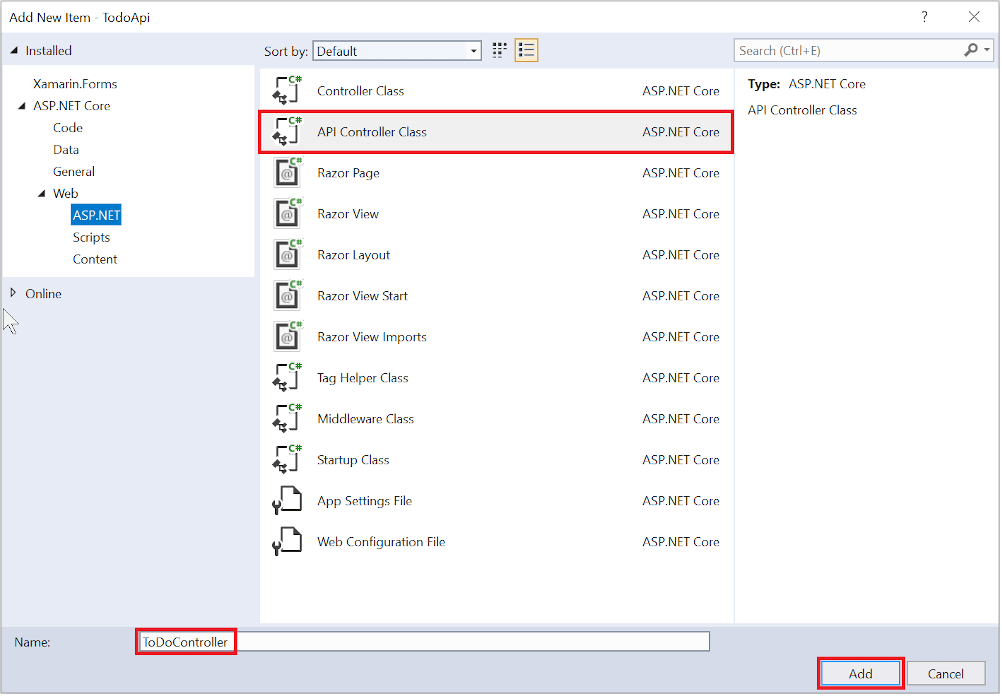
In the Add New Item dialog, select the API Controller Class template.
Name the class TodoController, and select Add.
Replace the template code with the following code:
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using TodoApi.Models;
namespace TodoApi.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class TodoController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly TodoContext _context;
public TodoController(TodoContext context)
{
_context = context;
if (_context.TodoItems.Count() == 0)
{
_context.TodoItems.Add(new TodoItem { Name = "Item1" });
_context.SaveChanges();
}
}
}
}
The preceding code:
- Defines an API controller class without methods.
- Decorates the class with the [ApiController] attribute. This attribute indicates that the controller responds to web API requests. For information about specific behaviors that the attribute enables, see Create web APIs with ASP.NET Core.
- Uses DI to inject the database context (
TodoContext) into the controller. The database context is used in each of the CRUD methods in the controller.
- Adds an item named
Item1 to the database if the database is empty. This code is in the constructor, so it runs every time there's a new HTTP request. If you delete all items, the constructor creates Item1 again the next time an API method is called. So it may look like the deletion didn't work when it actually did work.
Add Get methods
To provide an API that retrieves to-do items, add the following methods to the TodoController class:
[HttpGet]
public async Task<ActionResult<IEnumerable<TodoItem>>> GetTodoItems()
{
return await _context.TodoItems.ToListAsync();
}
[HttpGet("{id}")]
public async Task<ActionResult<TodoItem>> GetTodoItem(long id)
{
var todoItem = await _context.TodoItems.FindAsync(id);
if (todoItem == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
return todoItem;
}
These methods implement two GET endpoints:
GET /api/todoGET /api/todo/{id}
Test the app by calling the two endpoints from a browser. For example:
https://localhost:<port>/api/todohttps://localhost:<port>/api/todo/1
The following HTTP response is produced by the call to GetTodoItems:
{
"id": 1,
"name": "Item1",
"isComplete": false
}
]
Routing and URL paths
The
[HttpGet] attribute denotes a method that responds to an HTTP GET request. The URL path for each method is constructed as follows:
In the following GetTodoItem method, "{id}" is a placeholder variable for the unique identifier of the to-do item. When GetTodoItem is invoked, the value of "{id}" in the URL is provided to the method in itsid parameter.
[HttpGet("{id}")]
public async Task<ActionResult<TodoItem>> GetTodoItem(long id)
{
var todoItem = await _context.TodoItems.FindAsync(id);
if (todoItem == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
return todoItem;
}
Return values
The return type of the
GetTodoItems and
GetTodoItem methods is
ActionResult<T> type. ASP.NET Core automatically serializes the object to
JSON and writes the JSON into the body of the response message. The response code for this return type is 200, assuming there are no unhandled exceptions. Unhandled exceptions are translated into 5xx errors.
ActionResult return types can represent a wide range of HTTP status codes. For example, GetTodoItem can return two different status values:
- If no item matches the requested ID, the method returns a 404 NotFound error code.
- Otherwise, the method returns 200 with a JSON response body. Returning
item results in an HTTP 200 response.
Test the GetTodoItems method
This tutorial uses Postman to test the web API.
Add a Create method
Add the following PostTodoItem method:
[HttpPost]
public async Task<ActionResult<TodoItem>> PostTodoItem(TodoItem item)
{
_context.TodoItems.Add(item);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return CreatedAtAction(nameof(GetTodoItem), new { id = item.Id }, item);
}
The preceding code is an HTTP POST method, as indicated by the
[HttpPost] attribute. The method gets the value of the to-do item from the body of the HTTP request.
The CreatedAtAction method:
Returns an HTTP 201 status code, if successful. HTTP 201 is the standard response for an HTTP POST method that creates a new resource on the server.
Adds a
Location header to the response. The
Location header specifies the URI of the newly created to-do item. For more information, see
10.2.2 201 Created.
References the GetTodoItem action to create the Location header's URI. The C# nameofkeyword is used to avoid hard-coding the action name in the CreatedAtAction call.
[HttpGet("{id}")]
public async Task<ActionResult<TodoItem>> GetTodoItem(long id)
{
var todoItem = await _context.TodoItems.FindAsync(id);
if (todoItem == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
return todoItem;
}
Test the PostTodoItem method
Build the project.
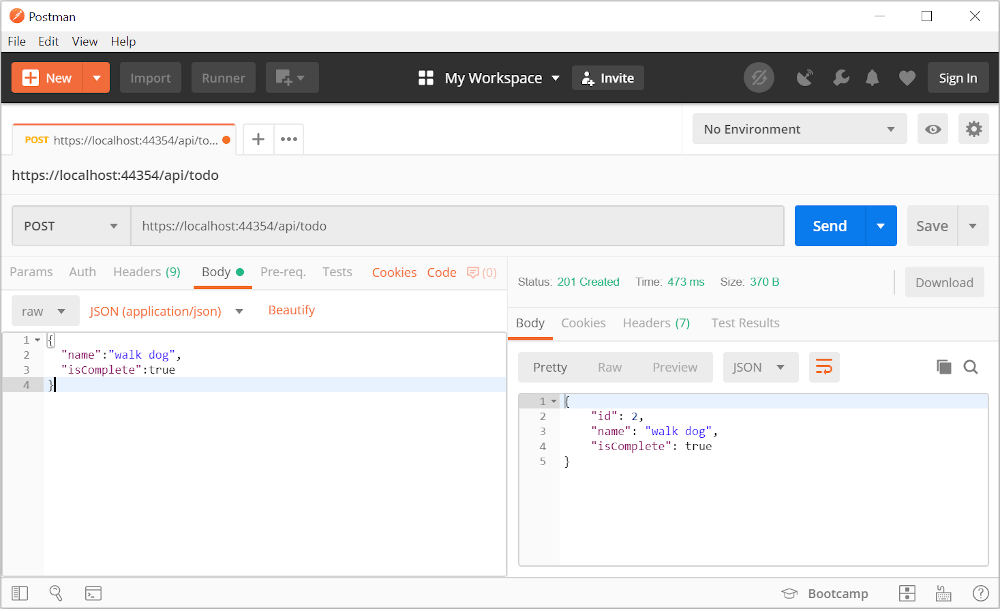
In Postman, set the HTTP method to POST.
Select the Body tab.
Select the raw radio button.
Set the type to JSON (application/json).
In the request body enter JSON for a to-do item:
"name":"walk dog",
"isComplete":true
}
Select Send.
If you get a 405 Method Not Allowed error, it's probably the result of not compiling the project after adding the PostTodoItem method.
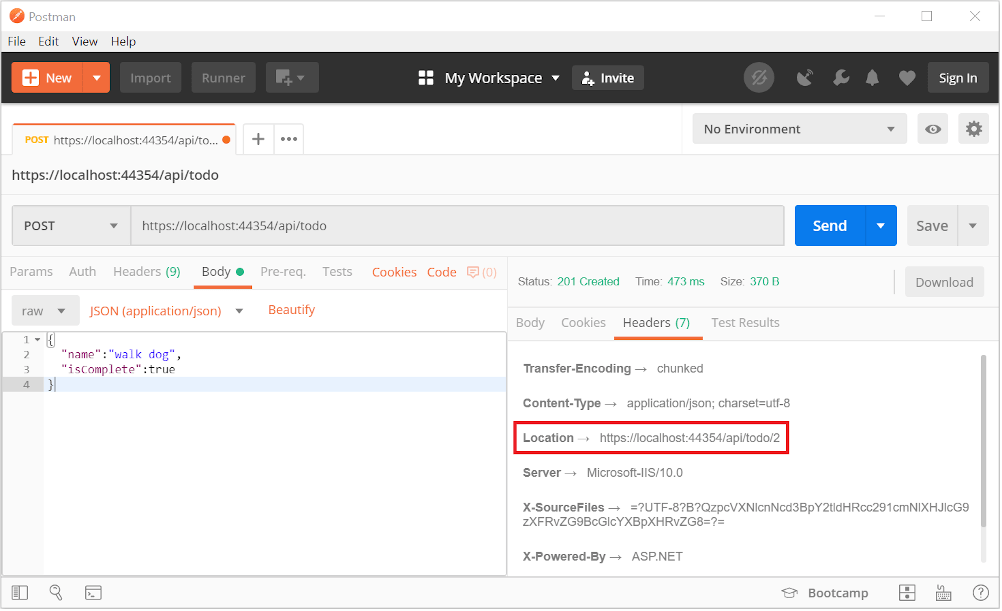
Select the Headers tab in the Response pane.
Copy the Location header value:
Set the method to GET.
Paste the URI (for example, https://localhost:5001/api/Todo/2)
Select Send.
Add a PutTodoItem method
Add the following PutTodoItem method:
[HttpPut("{id}")]
public async Task<IActionResult> PutTodoItem(long id, TodoItem item)
{
if (id != item.Id)
{
return BadRequest();
}
_context.Entry(item).State = EntityState.Modified;
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return NoContent();
}
PutTodoItem is similar to
PostTodoItem, except it uses HTTP PUT. The response is
204 (No Content). According to the HTTP specification, a PUT request requires the client to send the entire updated entity, not just the changes. To support partial updates, use
HTTP PATCH.
If you get an error calling PutTodoItem, call GET to ensure there's an item in the database.
Test the PutTodoItem method
This sample uses an in-memory database that must be initialed each time the app is started. There must be an item in the database before you make a PUT call. Call GET to insure there's an item in the database before making a PUT call.
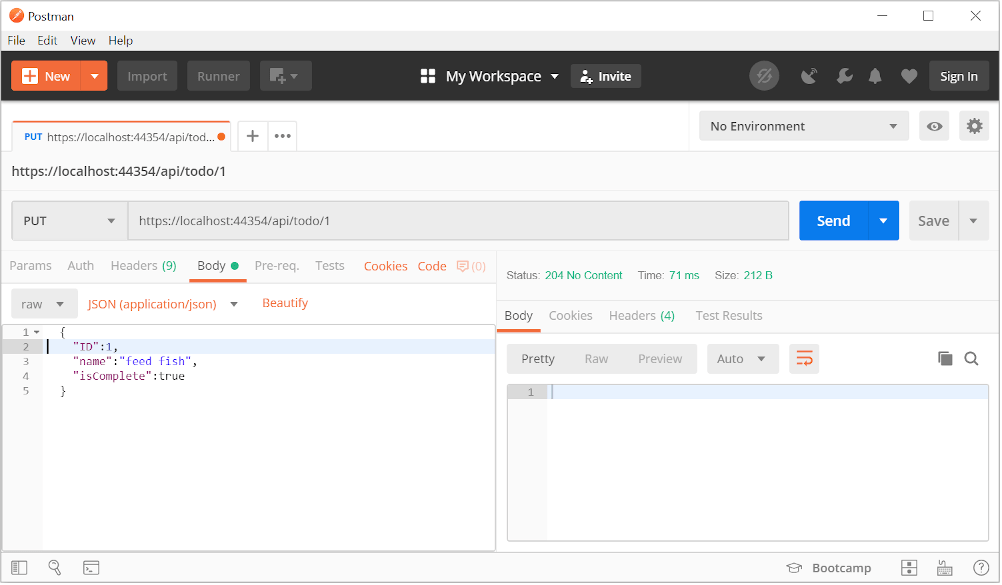
Update the to-do item that has id = 1 and set its name to "feed fish":
"ID":1,
"name":"feed fish",
"isComplete":true
}
The following image shows the Postman update:
Add a DeleteTodoItem method
Add the following DeleteTodoItem method:
[HttpDelete("{id}")]
public async Task<IActionResult> DeleteTodoItem(long id)
{
var todoItem = await _context.TodoItems.FindAsync(id);
if (todoItem == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
_context.TodoItems.Remove(todoItem);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return NoContent();
}
Test the DeleteTodoItem method
Use Postman to delete a to-do item:
- Set the method to
DELETE.
- Set the URI of the object to delete, for example
https://localhost:5001/api/todo/1
- Select Send
The sample app allows you to delete all the items. However, when the last item is deleted, a new one is created by the model class constructor the next time the API is called.
Call the API with jQuery
In this section, an HTML page is added that uses jQuery to call the web api. jQuery initiates the request and updates the page with the details from the API's response.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
else
{
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseDefaultFiles();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseMvc();
}
Create a wwwroot folder in the project directory.
Add an HTML file named index.html to the wwwroot directory. Replace its contents with the following markup:
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>To-do CRUD</title>
<style>
input[type='submit'], button, [aria-label] {
cursor: pointer;
}
#spoiler {
display: none;
}
table {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
border: 1px solid;
border-collapse: collapse;
}
th {
background-color: #0066CC;
color: white;
}
td {
border: 1px solid;
padding: 5px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>To-do CRUD</h1>
<h3>Add</h3>
<form action="javascript:void(0);" method="POST" onsubmit="addItem()">
<input type="text" id="add-name" placeholder="New to-do">
<input type="submit" value="Add">
</form>
<div id="spoiler">
<h3>Edit</h3>
<form class="my-form">
<input type="hidden" id="edit-id">
<input type="checkbox" id="edit-isComplete">
<input type="text" id="edit-name">
<input type="submit" value="Save">
<a onclick="closeInput()" aria-label="Close">✖</a>
</form>
</div>
<p id="counter"></p>
<table>
<tr>
<th>Is Complete</th>
<th>Name</th>
<th></th>
<th></th>
</tr>
<tbody id="todos"></tbody>
</table>
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.3.1.min.js"
integrity="sha256-FgpCb/KJQlLNfOu91ta32o/NMZxltwRo8QtmkMRdAu8="
crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="site.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
Add a JavaScript file named site.js to the wwwroot directory. Replace its contents with the following code:
let todos = null;
function getCount(data) {
const el = $("#counter");
let name = "to-do";
if (data) {
if (data > 1) {
name = "to-dos";
}
el.text(data + " " + name);
} else {
el.text("No " + name);
}
}
$(document).ready(function() {
getData();
});
function getData() {
$.ajax({
type: "GET",
url: uri,
cache: false,
success: function(data) {
const tBody = $("#todos");
$(tBody).empty();
getCount(data.length);
$.each(data, function(key, item) {
const tr = $("<tr></tr>")
.append(
$("<td></td>").append(
$("<input/>", {
type: "checkbox",
disabled: true,
checked: item.isComplete
})
)
)
.append($("<td></td>").text(item.name))
.append(
$("<td></td>").append(
$("<button>Edit</button>").on("click", function() {
editItem(item.id);
})
)
)
.append(
$("<td></td>").append(
$("<button>Delete</button>").on("click", function() {
deleteItem(item.id);
})
)
);
tr.appendTo(tBody);
});
todos = data;
}
});
}
function addItem() {
const item = {
name: $("#add-name").val(),
isComplete: false
};
$.ajax({
type: "POST",
accepts: "application/json",
url: uri,
contentType: "application/json",
data: JSON.stringify(item),
error: function(jqXHR, textStatus, errorThrown) {
alert("Something went wrong!");
},
success: function(result) {
getData();
$("#add-name").val("");
}
});
}
function deleteItem(id) {
$.ajax({
url: uri + "/" + id,
type: "DELETE",
success: function(result) {
getData();
}
});
}
function editItem(id) {
$.each(todos, function(key, item) {
if (item.id === id) {
$("#edit-name").val(item.name);
$("#edit-id").val(item.id);
$("#edit-isComplete")[0].checked = item.isComplete;
}
});
$("#spoiler").css({ display: "block" });
}
$(".my-form").on("submit", function() {
const item = {
name: $("#edit-name").val(),
isComplete: $("#edit-isComplete").is(":checked"),
id: $("#edit-id").val()
};
$.ajax({
url: uri + "/" + $("#edit-id").val(),
type: "PUT",
accepts: "application/json",
contentType: "application/json",
data: JSON.stringify(item),
success: function(result) {
getData();
}
});
closeInput();
return false;
});
function closeInput() {
$("#spoiler").css({ display: "none" });
}
A change to the ASP.NET Core project's launch settings may be required to test the HTML page locally:
- Open Properties\launchSettings.json.
- Remove the
launchUrl property to force the app to open at index.html—the project's default file.
There are several ways to get jQuery. In the preceding snippet, the library is loaded from a CDN.
This sample calls all of the CRUD methods of the API. Following are explanations of the calls to the API.
Get a list of to-do items
The jQuery
ajax function sends a
GET request to the API, which returns JSON representing an array of to-do items. The
success callback function is invoked if the request succeeds. In the callback, the DOM is updated with the to-do information.
getData();
});
function getData() {
$.ajax({
type: "GET",
url: uri,
cache: false,
success: function(data) {
const tBody = $("#todos");
$(tBody).empty();
getCount(data.length);
$.each(data, function(key, item) {
const tr = $("<tr></tr>")
.append(
$("<td></td>").append(
$("<input/>", {
type: "checkbox",
disabled: true,
checked: item.isComplete
})
)
)
.append($("<td></td>").text(item.name))
.append(
$("<td></td>").append(
$("<button>Edit</button>").on("click", function() {
editItem(item.id);
})
)
)
.append(
$("<td></td>").append(
$("<button>Delete</button>").on("click", function() {
deleteItem(item.id);
})
)
);
tr.appendTo(tBody);
});
todos = data;
}
});
}
Add a to-do item
The
ajax function sends a
POST request with the to-do item in the request body. The
accepts and
contentType options are set to
application/json to specify the media type being received and sent. The to-do item is converted to JSON by using
JSON.stringify. When the API returns a successful status code, the
getData function is invoked to update the HTML table.
const item = {
name: $("#add-name").val(),
isComplete: false
};
$.ajax({
type: "POST",
accepts: "application/json",
url: uri,
contentType: "application/json",
data: JSON.stringify(item),
error: function(jqXHR, textStatus, errorThrown) {
alert("Something went wrong!");
},
success: function(result) {
getData();
$("#add-name").val("");
}
});
}
Update a to-do item
Updating a to-do item is similar to adding one. The url changes to add the unique identifier of the item, and the type is PUT.
url: uri + "/" + $("#edit-id").val(),
type: "PUT",
accepts: "application/json",
contentType: "application/json",
data: JSON.stringify(item),
success: function(result) {
getData();
}
});
Delete a to-do item
Deleting a to-do item is accomplished by setting the type on the AJAX call to DELETE and specifying the item's unique identifier in the URL.
url: uri + "/" + id,
type: "DELETE",
success: function(result) {
getData();
}
});
Additional resources